A Path-Integral-Based Reinforcement Learning Algorithm for Path Following of an Auto-Assembly Mobile Robot
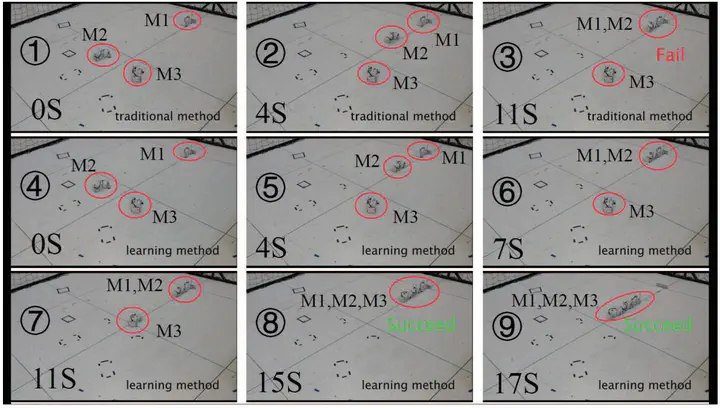 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: Unsplash
Abstract
Reinforcement learning (RL) combined with deep neural networks has led to a number of great achievements for robot control in virtual computer environments, where sufficient data can be obtained without any difficulty to train various models. However, thus far, only few and relatively simple tasks have been accomplished for practical robots, which is mainly caused by the following two reasons. First, training with real robots, especially with dynamic systems, is too complicated to be fully and accurately represented in simulations. Second, it is very costly to obtain training data from real systems. To address these two problems effectively, in this article, a path-integral-based RL algorithm is proposed for the task of path following of an autoassembly mobile robot, wherein three kernel techniques are introduced. First, a generalized path-integral-control approach is proposed to obtain the numerical solution of a stochastic dynamical system, wherein the calculation of the gradient and kinematics inverse is avoided to ensure fast and reliable training convergence. Second, a novel parameterization method using Lyapunov techniques is introduced into the RL algorithm to ensure good performance of the system when directly transferring simulation results into practical systems. Third, the optimal parameters for all discrete initial states are first learned offline and then tuned online to improve the generalization and real-time performance. In addition to the optimization control for the mobile robot, the proposed method also possesses general applicability for a class of nonlinear systems such as crane systems. Simulation and experimental results are included and analyzed to illustrate the superior performance of the proposed algorithm.